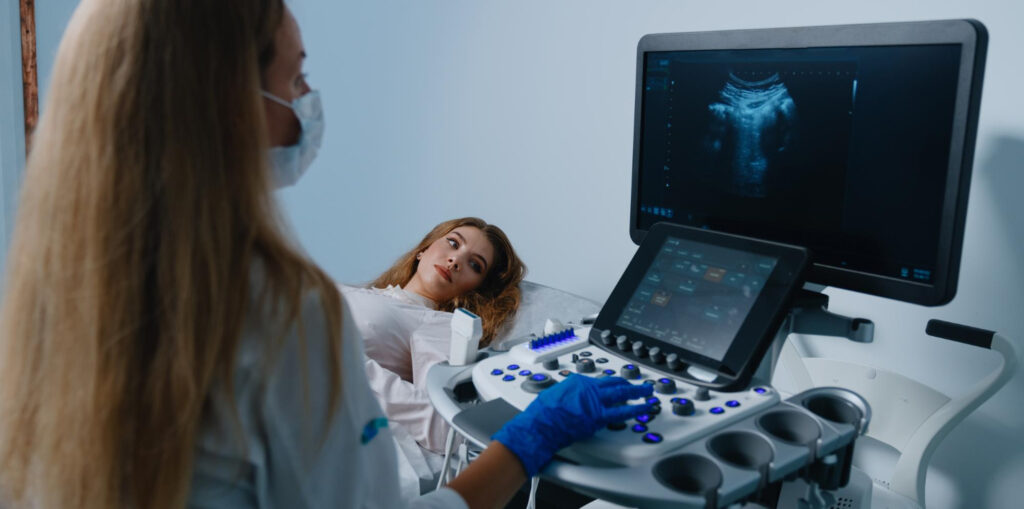
Fetal ultrasound scans, also known as pregnancy scans, are invaluable imaging procedures utilizing high-frequency sound waves to capture images of the developing baby within the mother’s womb. Lasting between 15 to 45 minutes, these scans play a crucial role in monitoring fetal development and identifying any potential complications during pregnancy.
Types of Fetal Ultrasound Scans:
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: This involves the insertion of a wand-like device into the vagina to capture detailed images, particularly useful when a transabdominal ultrasound doesn’t provide sufficient information.
- Transabdominal Ultrasound: Conducted by moving a transducer over the abdomen, this scan offers a broader view of the fetus and surrounding structures.
Why Fetal Ultrasound Scans Are Necessary:
Fetal ultrasound scans are essential components of prenatal care, serving multiple purposes:
- Confirmation of Pregnancy and Location
- Determination of Embryo Count (e.g., Twins or Triplets)
- Evaluation of Fetal Growth and Amniotic Fluid Levels
- Estimation of Gestational Age
- Assessment of Fetal Position for Delivery
- Detection of Birth Defects or Pregnancy Complications
- Monitoring of Fetal Movement, Breathing, and Heart Rate
Procedure Overview:
During a transabdominal scan, a clear gel is applied to the belly, and the transducer is moved to capture images. For a transvaginal scan, the patient lies on their back, and a vaginal probe captures images internally.
Preparation Tips:
- For a transvaginal ultrasound, a partially filled bladder may be required for clearer images.
- Drinking plenty of water before a transabdominal ultrasound aids in visualization.
- Sonographers generally prefer an empty bladder during second and third-trimester scans.
Comfort and Safety:
Ultrasound scans are painless procedures, with minimal discomfort from pressure on the abdomen by the transducer. They are safe, widely used, and require no special preparation.
Distinguishing Growth Scans:
While a growth scan is a type of ultrasound specifically assessing fetal growth and development, not all ultrasounds performed during pregnancy are growth scans. Other types of sonograms serve various purposes, such as confirming pregnancy, checking for complications, or determining fetal position.
In Conclusion:
Fetal ultrasound scans are integral to monitoring pregnancy, providing expectant parents and healthcare providers with vital information about fetal health and development. They are safe, non-invasive, and invaluable tools for ensuring a healthy pregnancy journey. Should any questions or concerns arise regarding ultrasound scans during pregnancy, consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable.

